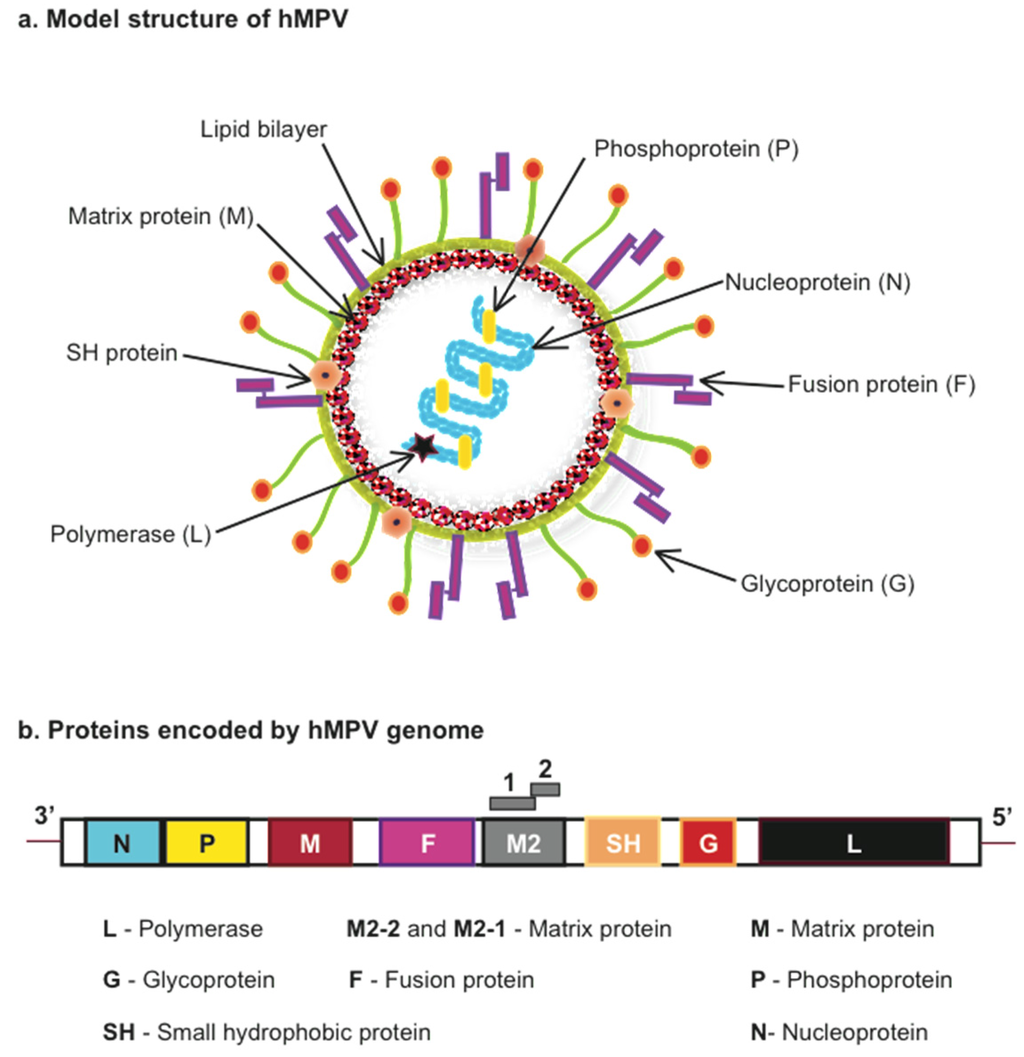
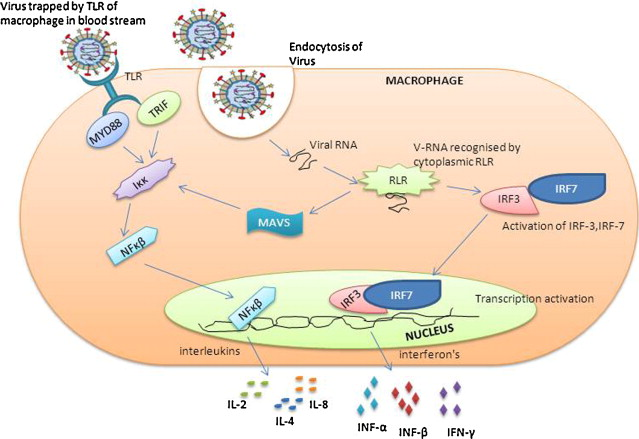
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that primarily affects individuals of all age groups, especially infants, children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. First identified in 2001, HMPV is known to cause respiratory tract infections ranging from mild cold-like symptoms to severe lower respiratory tract illnesses such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of HMPV infection typically include fever, cough, runny nose, sore throat, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, especially in vulnerable populations, HMPV can lead to pneumonia or exacerbate pre-existing respiratory conditions. Symptoms usually appear within 2 to 8 days after exposure to the virus.
Transmission:
HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Additionally, the virus can survive on surfaces for several hours, making indirect transmission possible through contact with contaminated objects. Crowded settings such as schools, daycare centers, hospitals, and nursing homes are common environments for HMPV transmission.
Prevention:
Preventing HMPV infection involves practicing good respiratory hygiene and adopting measures to reduce transmission. These include:
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Respiratory Etiquette: Covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets.
- Avoiding Close Contact: Limiting close contact with individuals showing symptoms of respiratory illness and avoiding crowded places during peak HMPV seasons.
- Cleaning and Disinfecting: Regularly cleaning and disinfecting frequently-touched surfaces and objects, particularly in communal areas and healthcare settings.
Diagnostic Testing for HMPV:
When suspecting a Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) infection, timely and accurate diagnostic testing is crucial for appropriate management. Diagnostic procedures typically involve the collection of respiratory specimens, such as nasopharyngeal swabs or nasal washes, from symptomatic individuals. These specimens are then subjected to various laboratory techniques to detect the presence of HMPV antigens or nucleic acids.
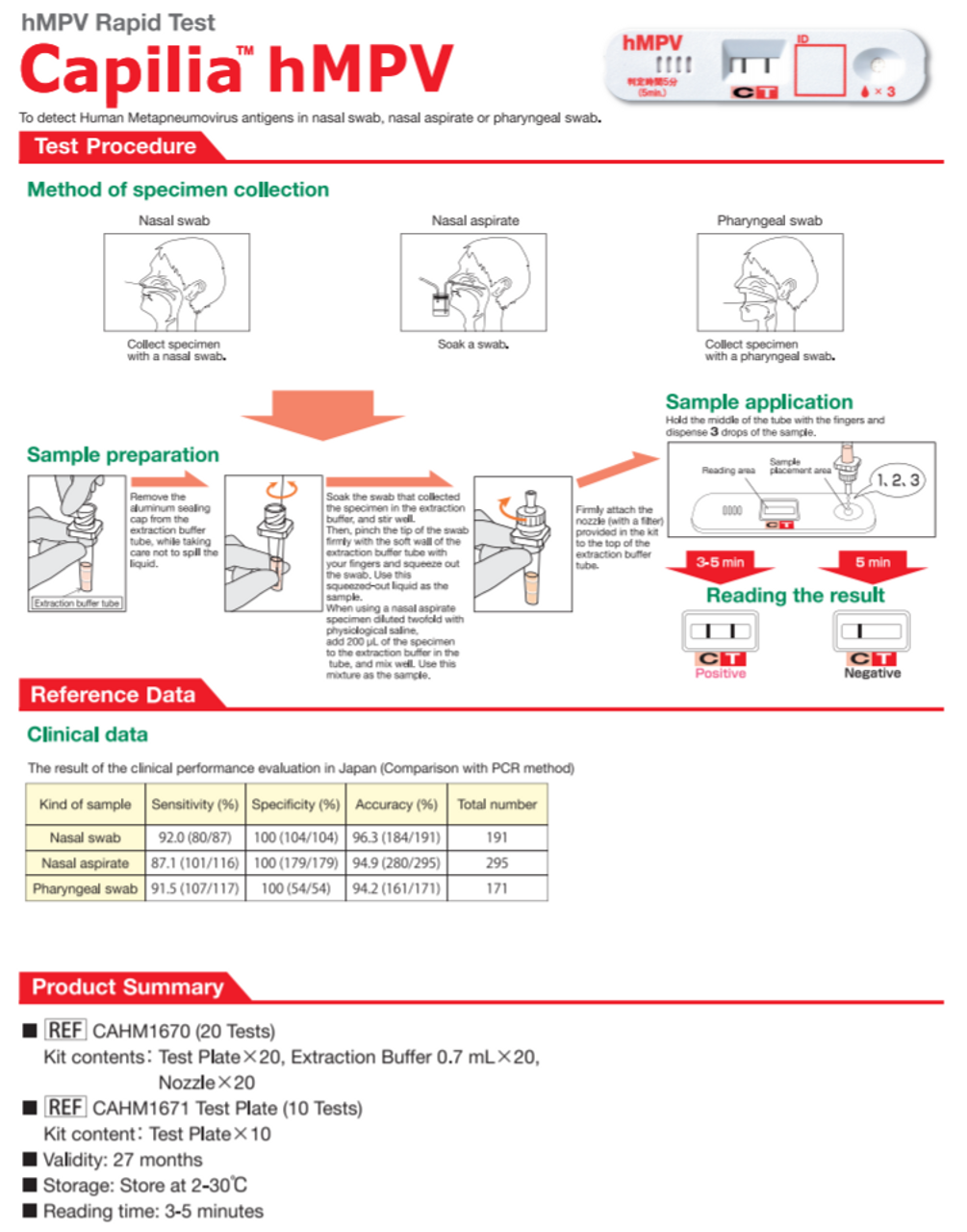
Rapid diagnostic tests for HMPV are available and play a significant role in expediting the diagnostic process. These tests offer quick results, usually within hours, allowing healthcare providers to promptly identify HMPV infections and initiate appropriate treatment and infection control measures. Rapid tests for HMPV often utilize immunofluorescence assays or molecular methods, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), to detect viral antigens or genetic material in respiratory samples.
While rapid diagnostic tests provide a valuable tool for the timely identification of HMPV infections, it's essential to interpret results in conjunction with clinical findings and epidemiological factors. Negative results from rapid tests do not rule out HMPV infection entirely, and confirmatory testing may be necessary in certain cases, particularly when clinical suspicion remains high.
Treatment:
There is currently no specific antiviral treatment for HMPV infection. Treatment typically focuses on managing symptoms and providing supportive care, such as adequate hydration and rest. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions or compromised immune systems.
Conclusion:
Human Metapneumovirus is a common respiratory virus that can cause a range of respiratory illnesses, particularly in vulnerable populations. Understanding the symptoms, transmission routes, and preventive measures is essential for reducing the spread of HMPV and minimizing its impact on public health. By practicing good respiratory hygiene and adopting preventive strategies, individuals can help protect themselves and others from HMPV infection.